In electrochemical experiments, it is not unusual to record the potential of a certain electrochemical system using one reference electrode but convert the data into a potential versus another reference electrode before reporting the results. Here, we show a quick and easy way of converting potentials between reference electrodes.
A table of common reference electrodes and their potentials vs. standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) can be easily found online. For this tutorial, we will use the table from Corrosion Doctors: http://corrosion-doctors.org/Corrosion-Thermodynamics/Reference-Half-Cells.htm
From the table in that link, we can see that the potential of a saturated Ag/AgCl reference electrode is +0.199V vs. SHE and the potential of a 1.0M calomel reference electrode is +0.280V vs. SHE.
For example, if the measured potential of our electrochemical system –0.460V with respect to Ag/AgCl, what is the potential with respect to SHE?
To find the answer, we can apply the following formula:
Where is the measured potential with respect to an Ag/AgCl reference, in this case, -0.460V and
is the potential of an Ag/AgCl reference electrode with respect to SHE, which is +0.199V.
Solving for , we get
Now, what is the measured potential with respect to 1.0M calomel?
We apply the same formula:
Solving for , we get
To convert potentials between Ag/AgCl and calomel reference electrodes directly, we can combine both equations:
Solving for , we get
Plugging in the numbers, we can see that the answers are the same:
In general, to convert potentials between 2 reference electrodes, we can do:
Then solve for .
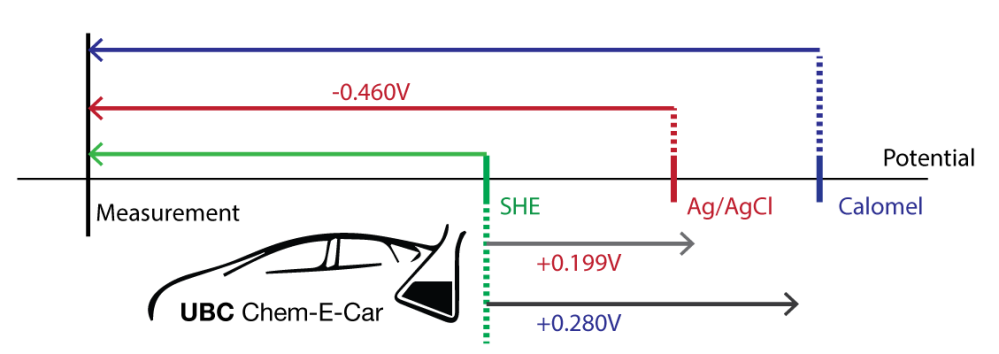
A derivation of this formula is best explained visually:
To find the measured potential vs SHE, we need to find the length of the green line (technically, it’s a vector, pointing left).
Based on the information we have, we can find the green vector by adding the red vector (pointing left, giving it a negative value) and the first grey vector (pointing right, therefore positive). In other words,
Similarly, finding the measured potential vs calomel is the same as finding the blue vector. We can do this by adding the difference of the 2 grey vectors to the red vector.
Some sites may give the potential of the reference electrode relative to NHE, RHE, SCE etc. instead of SHE. As long as the potentials given are with respect to the same electrode, the calculations are not affected.
Check back regularly for more electrochemistry updates!
Written by:
The UBC Chem-E-Car Battery Team
Siang, Tampriye, Andy, William